Applications of Big Data
Introduction to Big Data
Big Data is characterized by its three Vs: volume, velocity, and variety. The term volume refers to the massive amount of data being generated every second, encompassing structured and unstructured data. Velocity pertains to the speed at which data is generated, collected, and processed. Variety encapsulates the diverse types of data, including text, images, videos, sensor readings, social media interactions, and more.
Traditionally, data was manageable and analyzed using conventional tools. However, the explosion of data in recent years has necessitated the development of advanced technologies and techniques to extract meaningful insights from these vast datasets. This is where Big Data comes into play, offering the potential to uncover patterns, correlations, and trends that were previously hidden.
Applications of Big Data
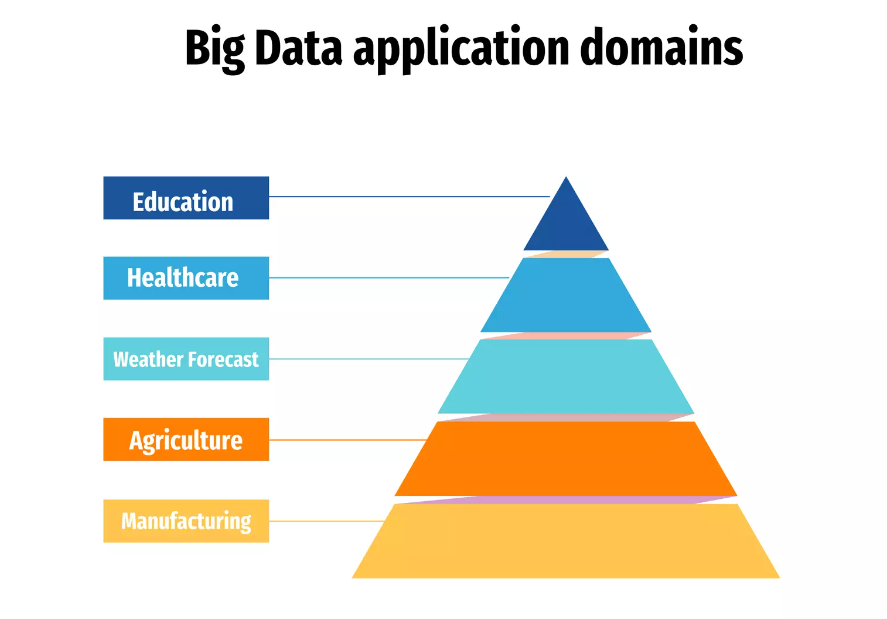
Healthcare and Medicine
Big Data has revolutionized healthcare and medicine by enabling personalized treatments, predicting disease outbreaks, and improving patient outcomes. Medical records, clinical trials, genomics data, and wearable devices generate enormous amounts of data that can be analyzed to develop targeted therapies, early diagnosis models, and more effective treatment plans.
Finance and Banking
In the financial sector, Big Data drives risk assessment, fraud detection, and customer insights. By analyzing transaction data, market trends, and social media sentiments, financial institutions can make informed decisions, tailor services to customer needs, and mitigate potential risks.
Retail and Marketing
Retailers leverage Big Data to enhance customer experiences, optimize inventory management, and create targeted marketing campaigns. Through analyzing purchase histories, online interactions, and demographic data, businesses can anticipate consumer preferences and tailor their offerings accordingly.
Must Read….
What is Big Data and Why is it Important in future aspects?
Manufacturing and Supply Chain
In manufacturing, Big Data is used for predictive maintenance, quality control, and supply chain optimization. Sensors and IoT devices collect real-time data from machinery, allowing for proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime. Additionally, analyzing supply chain data optimizes inventory levels and reduces wastage.
Energy and Utilities
Big Data aids in energy production and consumption optimization. Smart grids gather data on energy consumption patterns, allowing for real-time adjustments in energy distribution. This leads to efficient energy utilization and reduced costs.
Transportation and Logistics
Logistics companies utilize Big Data to optimize routes, predict delivery times, and enhance fleet management. By analyzing traffic patterns, weather conditions, and transportation data, businesses can minimize delivery delays and optimize resource allocation.
Agriculture and Environmental Monitoring
Big Data is transforming agriculture through precision farming. Sensor data from fields provide insights into soil quality, moisture levels, and crop health. This enables farmers to make data-driven decisions to improve crop yield and resource efficiency. Additionally, environmental monitoring systems use Big Data to track climate change and predict natural disasters.
Government and Public Services
Governments leverage Big Data for urban planning, disaster response, and public safety. Data from sensors, social media, and public records enable authorities to predict traffic congestion, allocate resources during emergencies, and enhance citizen services.
Challenges and Considerations
While the applications of Big Data are extensive and promising, they come with challenges. Privacy concerns, data security, and ethical considerations are paramount, especially when dealing with sensitive information. Additionally, the sheer volume of data requires sophisticated storage and processing solutions. Data quality and interoperability issues also need to be addressed to ensure accurate analyses and meaningful insights.
The applications of Big Data are wide-ranging and transformative, touching nearly every sector of the modern world. From healthcare advancements to optimized logistics, Big Data’s potential to unlock insights and drive innovation is immense. However, as we continue to harness the power of Big Data, it’s crucial to address the challenges and ethical considerations that arise. By doing so, we can ensure that we navigate the data-rich landscape responsibly, reaping its benefits while safeguarding privacy and security. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the potential of Big Data to reshape industries and enhance our understanding of the complex world we inhabit.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is Big Data?
A1: Big Data refers to the massive volume, velocity, and variety of data generated and collected from various sources. It encompasses structured and unstructured data, and its analysis can yield valuable insights and trends.
Q2: How is Big Data used in healthcare?
A2: In healthcare, Big Data is used to personalize treatments, predict disease outbreaks, and improve patient outcomes. It involves analyzing medical records, genomics data, and wearable device information.
Q3: What role does Big Data play in finance?
A3: Big Data is crucial in finance for risk assessment, fraud detection, and customer insights. It involves analyzing transaction data, market trends, and social media sentiments.
Q4: How does Big Data impact retail and marketing?
A4: Retailers use Big Data to enhance customer experiences, optimize inventory management, and create targeted marketing campaigns. It involves analyzing purchase histories, online interactions, and demographic data.
Q5: How does Big Data optimize transportation logistics?
A5: Big Data optimizes transportation logistics by analyzing traffic patterns, weather conditions, and transportation data. This helps in route optimization, predicting delivery times, and efficient resource allocation.
Q6: What challenges are associated with Big Data?
A6: Challenges of Big Data include privacy concerns, data security, ethical considerations, data quality issues, and the need for advanced storage and processing solutions.