Big Data Technology
Introduction
In today’s digital age, an unprecedented volume of data is generated, stored, and analyzed, reshaping the way industries and societies function. This phenomenon is aptly termed “Big Data.” It encompasses the vast amounts of information produced by our digital interactions, machines, sensors, and various other sources. Big Data isn’t just a buzzword; it represents a paradigm shift that has profound implications for businesses, governments, science, healthcare, and society as a whole. This article delves into the concept of Big Data, its importance in various domains, and its future prospects.
Understanding Big Data
Big Data is characterized by the three V’s: Volume, Velocity, and Variety.
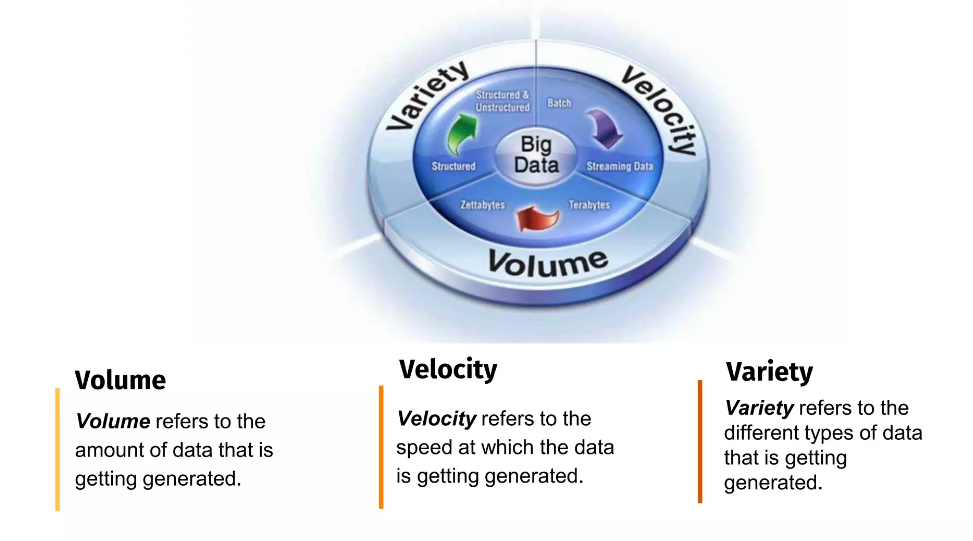
- Volume: The sheer volume of data being generated daily is staggering. Traditional databases struggle to handle this scale. With the advent of the Internet of Things (IoT), smartphones, and social media platforms, data production has skyrocketed.
- Velocity: The speed at which data is generated and collected is unprecedented. Social media posts, sensor readings, financial transactions – all of these generate data in real-time.
- Variety: Big Data isn’t just structured information like traditional databases. It encompasses unstructured and semi-structured data as well – text, images, videos, social media posts, and more.
Read also…
The Evolution of Artificial Intelligence: Complete History
Apart from the three V’s, Big Data also involves the concept of veracity (data quality), value (extracting insights), and variability (inconsistent data flows).
Importance of Big Data
- In Business and Marketing: Big Data has revolutionized business strategies. Companies can analyze consumer behavior, preferences, and trends to tailor products and marketing campaigns. This personalization enhances customer experiences and drives revenue growth.
- Healthcare and Medicine: Big Data analysis can lead to breakthroughs in medical research and patient care. It helps in disease prediction, drug discovery, and treatment optimization. Wearable devices and health apps contribute to continuous health data collection.
- Scientific Research: In fields like astronomy, genomics, and climate science, Big Data facilitates data-intensive research. It enables scientists to process and analyze vast datasets, leading to new insights and discoveries.
- Urban Planning and Smart Cities: With urbanization on the rise, Big Data aids in managing city resources efficiently. It enables predictive analysis of traffic patterns, energy consumption, waste management, and more.
- Finance and Banking: Fraud detection, risk assessment, and algorithmic trading are areas where Big Data is extensively employed. Real-time data analysis helps financial institutions make informed decisions.
- Government and Public Policy: Governments use Big Data for policy formulation, disaster management, and public health monitoring. It enhances decision-making by providing accurate and up-to-date information.
- Entertainment and Media: Streaming platforms utilize Big Data to understand user preferences, suggesting content tailored to individual tastes. This improves user engagement and platform retention.
Must read..
Automating Website Change Notifications via Email using Python
Future Implications of Big Data
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration: The synergy between Big Data and AI/ML is undeniable. Machine learning algorithms thrive on data, and as Big Data grows, AI capabilities will only advance further. This convergence will drive innovations in automation, predictive analytics, and personalized experiences.
- Ethical and Privacy Concerns: As Big Data expands, concerns about data privacy, security, and misuse amplify. Striking a balance between data utilization and individual privacy rights will be a critical challenge.
- Healthcare Revolution: The healthcare sector stands to benefit immensely from ongoing Big Data advancements. Personalized medicine, early disease detection, and efficient patient care will become more achievable.
- Environmental Sustainability: Big Data can play a pivotal role in monitoring and mitigating environmental issues. From tracking deforestation to predicting natural disasters, data-driven insights will aid in preserving the planet.
- Smarter Cities: The concept of smart cities will flourish as Big Data enables urban planning to be more responsive and sustainable. Traffic management, energy conservation, and waste reduction will be optimized.
- Education Transformation: Personalized learning paths for students, data-driven insights for educators, and efficient administrative processes are potential outcomes of incorporating Big Data into education.
- Advancements in Research: Big Data will continue to drive scientific breakthroughs. Fields like genetics, particle physics, and climate modeling will benefit from data-intensive analysis.
In a world dominated by data, the era of Big Data has profound implications for every facet of human existence. Its capacity to transform industries, enhance decision-making, and unlock new opportunities is undeniable. The future holds the promise of AI integration, ethical considerations, healthcare revolutions, and more sustainable societies. As we navigate the evolving landscape of Big Data, it is imperative to harness its power responsibly, ensuring a harmonious coexistence of technology and humanity. Embracing the challenges and opportunities presented by Big Data will shape the course of innovation and progress in the decades to come.
FAQs
1. What is Big Data?
Big Data refers to the vast and complex sets of data that are generated at an unprecedented volume, velocity, and variety. It encompasses structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data, requiring advanced tools and techniques for storage, processing, and analysis.
2. What are the three V’s of Big Data?
The three V’s of Big Data are Volume (the sheer amount of data), Velocity (the speed at which data is generated and processed), and Variety (the diverse types of data, including text, images, videos, etc.).
3. How is Big Data collected?
Big Data is collected from various sources such as social media, sensors, IoT devices, transaction records, and more. This data is then stored, processed, and analyzed to extract valuable insights.
4. Why is Big Data important?
Big Data is crucial because it enables businesses to make informed decisions, enhances scientific research, improves healthcare outcomes, optimizes resource management, and empowers governments to create effective policies based on data-driven insights.
5. What is the role of AI and Machine Learning in Big Data?
AI and Machine Learning play a significant role in Big Data by analyzing large datasets to identify patterns, trends, and correlations that humans might miss. They automate decision-making processes and contribute to the creation of predictive models.
6. How does Big Data impact business?
Big Data transforms businesses by providing insights into customer behavior, enabling targeted marketing, improving supply chain efficiency, optimizing operations, and fostering innovation through data-driven strategies.
7. What are the challenges of working with Big Data?
Challenges include data privacy and security concerns, data quality assurance, managing the sheer volume of data, scalability of infrastructure, and ensuring ethical use of data.
8. What are some examples of Big Data applications?
Examples include personalized recommendations on streaming platforms, real-time traffic monitoring and optimization in smart cities, fraud detection in financial services, and disease prediction in healthcare.
9. How does Big Data impact healthcare?
Big Data in healthcare helps in early disease detection, personalized treatment plans, drug discovery, and efficient patient care. It also contributes to research and development in medical science.
10. What is the future of Big Data?
the future of Big Data involves deeper integration with AI and Machine Learning, addressing ethical and privacy concerns, enabling more personalized experiences, revolutionizing healthcare, advancing environmental sustainability efforts, and driving scientific discoveries.
11. How does Big Data influence urban planning?
Big Data aids urban planning by analyzing data on traffic patterns, energy consumption, waste management, and more, leading to smarter and more sustainable city development.
12. How can businesses ensure ethical use of Big Data?
Businesses should establish clear data usage policies, obtain proper consent from users, anonymize sensitive data, and comply with data protection regulations to ensure ethical use of Big Data.
13. What are some tools used for processing Big Data?
tools include Apache Hadoop, Apache Spark, NoSQL databases like MongoDB, data visualization tools like Tableau, and cloud-based platforms such as AWS and Azure.
14. How does Big Data contribute to scientific research?
Big Data facilitates data-intensive research in fields like genomics, astronomy, climate science, and more. It enables scientists to process and analyze massive datasets, leading to new insights and discoveries.
15. What are the potential risks of Big Data?
Risks include privacy breaches, misuse of personal data, algorithmic biases, and the possibility of making incorrect decisions based on flawed analysis.
Essential Tips for Staying Hydrated During Summer – Your Ultimate Guide