History of Artificial Intelligence:
In the fast-paced realm of technology, the evolution of artificial intelligence (AI) stands as one of the most intriguing and transformative journeys. From its humble beginnings in ancient myths to its modern-day applications in our daily lives, AI has traversed a remarkable path. In this article, we delve into the captivating history of AI, exploring key milestones, breakthroughs, and the societal impact that has shaped its trajectory.
1. Ancient Roots and Turing’s Vision
The history of AI traces its roots back to ancient civilizations, where tales of mechanical beings and automated entities hinted at the human desire to replicate intelligence. However, the true foundation of modern AI was laid in 1950 when the eminent mathematician and computer scientist Alan Turing introduced the concept of the Turing Test. This benchmark challenged scientists to create machines capable of exhibiting intelligence indistinguishable from that of humans.
2. The Dartmouth Workshop and the Birth of AI
The pivotal moment that gave birth to the term “artificial intelligence” occurred in 1956 at the Dartmouth Workshop. A group of pioneering researchers convened to discuss and explore the possibilities of creating machines with human-like intelligence. This workshop marked the official initiation of AI as a formal field of study and research.
Must Read…….
The Future of Artificial Intelligence: A Journey of Possibilities
3. Early AI Pioneers and Symbolic Logic
The 1950s and 1960s witnessed remarkable progress in AI research. Visionaries like Allen Newell and Herbert A. Simon developed the Logic Theorist, a program capable of proving mathematical theorems using formal logic. This symbolic approach laid the groundwork for subsequent advancements in AI reasoning and decision-making.
4. Symbolic AI and Expert Systems
The subsequent decades saw the rise of symbolic AI, which revolved around manipulating symbols to simulate human thought processes. Expert systems, a notable manifestation of symbolic AI, emulate the expertise of human specialists in specific domains. These systems showcased AI’s potential in problem-solving and decision-making tasks.
5. The AI Winter: Challenges and Resilience
Despite the promising advancements, the field of AI encountered a period known as the “AI winter” during the 1970s and 1980s. Unrealistic expectations and a lack of significant breakthroughs led to reduced funding and dwindling interest in AI research. However, the resilience of dedicated researchers ensured that the flame of AI innovation was never completely extinguished.
6. Connectionism and Neural Networks Resurgence
The 1980s and 1990s heralded the resurgence of interest in neural networks and connectionism. Researchers like Geoffrey Hinton and Yann LeCun contributed to the development of neural networks, which sought to mimic the brain’s architecture. This period laid the foundation for breakthroughs in image recognition, speech processing, and pattern recognition.
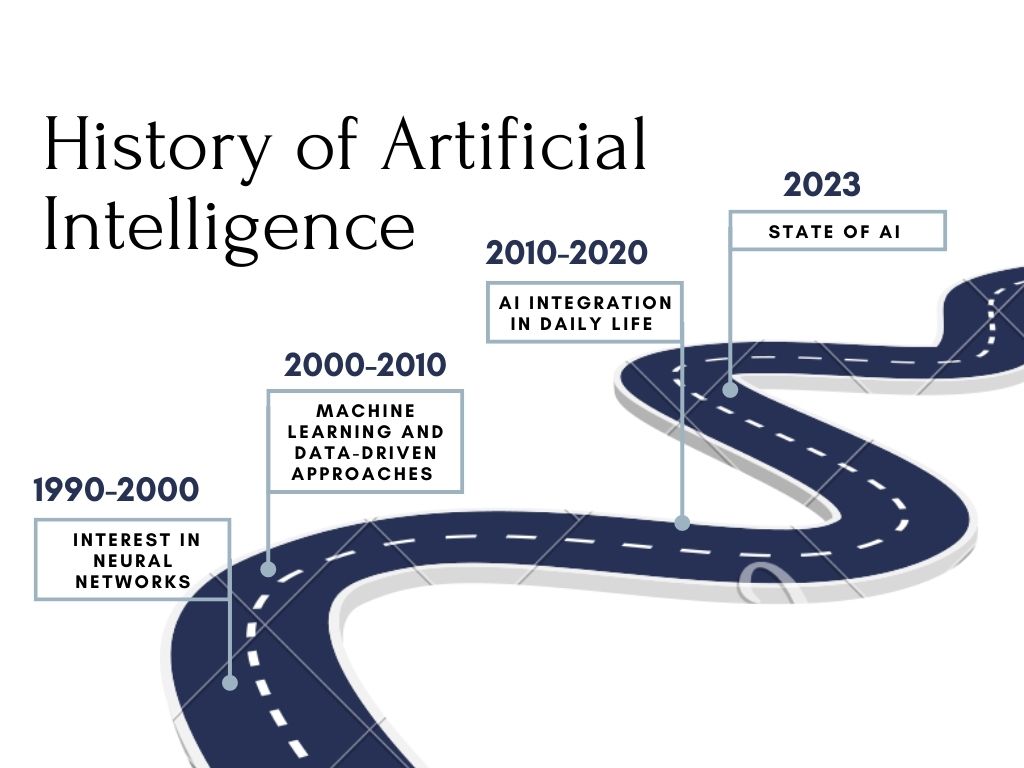
7. Machine Learning and Data-Driven Paradigms
The turn of the millennium marked a significant shift towards machine learning and data-driven approaches. Techniques such as support vector machines and random forests gained prominence for their ability to make sense of vast datasets. AI applications began permeating diverse industries, from finance to healthcare.
8. The Deep Learning Revolution
The 2010s witnessed the meteoric rise of deep learning, a subset of machine learning characterized by neural networks with multiple layers. Deep learning models revolutionized fields like image classification, natural language processing, and even game-playing. The advent of big data and powerful computing accelerated the capabilities of these models, reshaping industries in the process.
Also Read….
How to Integrate IP Camera in YOLO Model: A Comprehensive Guide for Enhanced Object Detection
9. AI in Everyday Life
As AI technologies mature, they seamlessly integrate into our daily lives. Virtual assistants like Siri and Google Assistant transformed how we interact with our devices, while recommendation systems on streaming platforms personalized content consumption. The impact of AI extended to healthcare, with improved diagnostics and personalized treatment plans.
10. Ethical and Societal Considerations
With great power comes great responsibility. The rapid advancements in AI have raised ethical concerns regarding bias, privacy, job displacement, and the potential for AI systems to operate beyond human control. These concerns prompted discussions and led to the development of ethical guidelines and regulations for responsible AI development and deployment.
11. The Current Landscape and Future Prospects
As of 2021–2023, the AI landscape continues to evolve rapidly. Reinforcement learning, generative models, and quantum computing are at the forefront of AI research. Conversational AI systems, powered by models like GPT-3.5, exhibit unparalleled language understanding and generation capabilities, enhancing human-machine interactions.
If You Want Interior Designers Must Read…
Best 10 Interior Designers & House Decorators in Florida
The journey of artificial intelligence has been a testament to human innovation and perseverance. From its ancient origins to its modern-day applications, AI has transformed how we perceive and interact with technology. As the field marches forward, it is crucial to maintain a delicate balance between technological advancement and ethical responsibility, ensuring that AI serves as a force for good in our ever-evolving world.
FAQs
1. What is the history of artificial intelligence (AI)?
The history of AI traces its origins from ancient myths and folklore to its formal inception in the mid-20th century. It has evolved through various phases of development, from early concepts and symbolic AI to the rise of machine learning and deep learning in the modern era.
2. When was the term “artificial intelligence” coined?
The term “artificial intelligence” was coined in 1956 during the Dartmouth Workshop, where researchers gathered to discuss the creation of machines that could exhibit human-like intelligence.
3. What is the Turing Test?
The Turing Test, proposed by Alan Turing in 1950, is a benchmark for evaluating a machine’s ability to display intelligent behavior indistinguishable from that of a human. It involves a human evaluator engaging in a natural language conversation with both a machine and a human, without knowing which is which.
4. What is symbolic AI?
Symbolic AI involves manipulating symbols and using logical reasoning to simulate human thought processes. This approach was prominent in the early years of AI research and was used to create expert systems capable of specialized decision-making.
5. What caused the “AI winter”?
The “AI winter” refers to a period of reduced interest and funding in AI research during the 1970s and 1980s. Unrealistic expectations, limited technological capabilities, and a lack of significant breakthroughs contributed to this downturn.
6. How did neural networks make a comeback?
Neural networks experienced a resurgence in the 1980s and 1990s due to advances in computing power and new learning algorithms. Researchers like Geoffrey Hinton and Yann LeCun played pivotal roles in reinvigorating the field of neural networks.
7. What is deep learning?
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that involves neural networks with multiple layers (deep neural networks). It has revolutionized AI by achieving exceptional performance in tasks like image recognition, natural language processing, and more.
8. How has AI impacted everyday life?
AI has become integral to daily life through applications like virtual assistants (Siri, Google Assistant), recommendation systems (Netflix, Amazon), and personalized healthcare. It has transformed how we interact with technology and made various tasks more efficient.
9. What are the ethical concerns surrounding AI?
Ethical concerns related to AI include bias in algorithms, privacy implications, potential job displacement due to automation, and the risk of AI systems operating autonomously without human control. Addressing these concerns is crucial for responsible AI development.
10. What is the current state of AI?
As of 2021-2023, AI is advancing rapidly. Breakthroughs in areas like reinforcement learning, generative models, and quantum computing are shaping the future of AI. Conversational AI models like GPT-3.5 exhibit advanced language understanding and generation capabilities.
11. What does the future hold for AI?
The future of AI is expected to involve continued advancements in various domains, including healthcare, autonomous systems, and AI ethics. AI’s potential to drive innovation across industries while addressing ethical considerations will play a crucial role in shaping its trajectory.
12. How can AI benefit society responsibly?
AI can benefit society by improving efficiency, providing personalized services, aiding in medical diagnoses, and addressing complex problems. Responsible development, transparency, and collaboration between researchers, policymakers, and industry stakeholders are key to harnessing AI’s potential for the greater good.